The Route of the tour
Planning a trip should be very exciting adventure
Scenery and historical sites along the way.
TripAdvisor Authentic Famagustian professional Driver and Tourist Guide
Discover Dividing Line – Buffer zone
View the Famagusta ghost town from the North
View the Famagusta ghost town from the South
Pick up points all over Ayia Napa and Protaras.
Visit Constantia Beach (ghost town Varosha) Famagusta. GUIDING THE GHOST TOWN FAMAGUSTA FROM INTO.
Free time to explore the old town of Famagusta.
Why Choose US
Years of experience as a tour guide.
Route Part 1
Discover The Ghost Town with Mr. John
The name Ayia Napa is derived from a Venetian-era monastery of the same name, located in the center of the town, next to the square that today is the clubbing centre.l2l The word “Ayia” means “holy” in Greek. “Napa” is archaic and means “wooded valley” or “dell”. In ancient times the area surrounding the town was covered with thick forest.
Ayia Napa lies near Cape Greco at the eastern part of Cyprus, south of Famagusta, and forms part of a larger area known as Kokkinochoria (“Red Villages”, a name derived from the vivid red colour of the soil). It is a town of the Famagusta District, in the remaining Greek-controlled southern part of the district, while the northern part has been occupied by Turkish forces since
1974.
Ayia Napa is about 12 kilometres (7.5 miles) from Protaras, a town that has seen similar development but still manages to remain low-key and more favourable for families and Cypriot locals.
Protaras (Greek: [Προταράς ]) is a predominantly tourist resort which comes under the administrative jurisdiction of Paralimni Municipality in Cyprus. In ancient times, where Protaras is now located, stood the old city-state of Leukolla.ll The city possessed a small safe harbour where Demetrius Poliorketes sought refuge in the year 306 BC, lying in wait for Ptolemy, one of the successors of Alexander the Great. Protaras is also referred to as “the land of windmills”, maintaining the nostalgic quality of the past.
Protaras has clear sky-blue waters and sandy beaches, the most well-known of which is Fig Tree Bay. Building on the success of Ayia Napa, located about 10 km (6 mi) southwest, it has expanded into a modern holiday resort of considerable size with tens of high capacity hotels, hotel apartments, villas, restaurants, pubs and associated facilities.
Protaras is a diving destination. Green Bay is the most popular dive site with thousands of first timers trying scuba skills Protaras most famous dive site for Technical Diving and Commercial Diver training is the Cyclops bay located on the border with Ayia Napa.
Kapparis is a coastal village in Cyprus near Paralimni and Protaras, and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) and part of the Famagusta district.
lt is a relatively new tourist town and under heavy construction and development of buildings, therefore, most buildings are new. There are some air raid shelters at Kapparis built during the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974.
Visitors from the UK and Greece come to the village on holiday, and there are a number of places to eat. There are several beaches in Kapparis including the famous beach called Fireman’s Beach.
*Kapparis is part of the Famagusta district which still a divided district and much of the area in Famagusta is occupied by TurkeyTurkey. The coastal road in Kapparis is called Kennedy Ave. fireman Beach


Route Part 2
Take in the scenery with Mr. John
Paralimni (Greek: Παραλιμνι) is a town within the Famagusta District of Cyprus, situated on the island’s east coast. Since the Turkish invasion in 1974, it has increased in size and status, primarily due to the migration of refugees fleeing from the north. Many workers in the tourist sectors of Protaras and Ayia Napa live in Paralimni, which is now the temporary administrative centre of the Famagusta District and the biggest municipality of the district under the control of the internationally-recognised government of Cyprus.
«The word Paralimni means “by the lake”. Historically, the town was built on the shores of a shallow lake which filled with water only in the winter. At the beginning of the 20th century, the whole lakebed was reclaimed for agricultural purposes.
Paralimni has not always been where it is now, and was built originally on a hill situated between Deryneia and its present location.
Deryneia (Greek: Δερύνεια) is a large village in the island of Cyprus. It is located at the east side of the island, 2 km (1 mi) south of the city of Famagusta. The population of the village is 5,758 (October 2011 census) and it consists of a municipality since 1994. The current mayor is Andros Karayiannis. Since the 1974 Turkish invasion of Cyprus, around 75% of the village terrain is in Northern Cyprus. The village is 12 kilometers from the famous resort of Ayia Napa.
The “Ghost Town” of Varosha can be clearly viewed from the roof of the Cultural Centre, as can the craters from shells fired during the invasion in the field opposite.
+ The village has agricultural land around it, and is one of the “Kokkinochoria” (red villages) so called from the red soil. Potatoes are widely grown but Deryneia is famous for its strawberries and holds a biennial strawberry festival at the
football ground of Anagennisi Deryneia on the Dherynia to Sotira road. Gazimagusa.
It has been named after the Lusignan monks that lived in Panayia of Hortanion, a nearby monastery and they were called Fremenors, as the Cypriot author Nearchos Klerides mentions in his book “Villages and Cities of Cyprus”.
«The monks could not support themselves and in 1468 they turned to Jacob, the Lusignan King of Cyprus who gave them a substantial sum of money. The village of Frenaros has its own Byzantine churches.
«Two of them, the Agios Andronikos and the Archangelos Michael dated back to the 12th century. The church of Ayia Marina has also some interesting frescoes.
Route part 3
Discover The History of the Ghost Town Famagusta with Mr. John
Located less than ten kilometers west of Famagusta and adjacent to the British Bases of Saint Nicholas or “four miles” as many call them. The village is situated geographically where Kokkinohoria end and the plain of Mesaoria begins.
«During the Turkish invasion of 1974 was occupied by the Turks on 31/8/1974. For the name of the village there is no specific credible version, documented in any way. Further south is the current District St. George Acheritou where many people from Acheritou and refugees from the surrounding villages were installed. After the tragic events of 1974, many residents of Acheritou took refuge in SEDIGEP packing plant which is in the S.B.A area.
A temporary school was set up with the help of the minister of education and refugee volunteers. Later in 1976-1977, most people moved to the refugee Community of Ayios Georgios Vrysoulles as it was first named.
Ayios Nikolaos Station (also spelled Agios Nikolaos; Greek: Άγιος Νικόλαος, lit. “Saint Nicholas”) is a British military station and part of in the British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia in Cyprus.
It is a former village (Ayios Nikolaos, SBA) connected by a road to the main area of the Dhekelia Garrison.
The Joint Service Signal Unit (Cyprus) (JSSU(Cyp)), formerly 9th Signal Regiment and the Royal Air Force’s 33 Signals Unit, is based at Ayios Nikolaos. This unit is a British Armed Forces run electronic intelligence gathering station. The station was established at Ayios Nikolaos shortly after the Second World War.
al 7
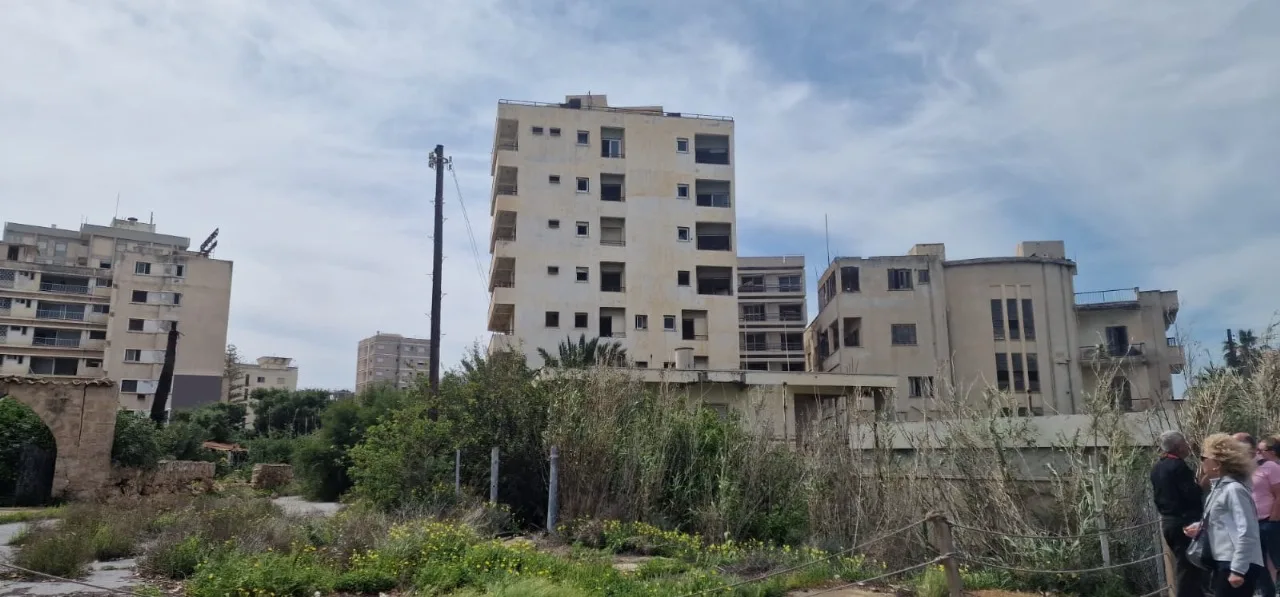
Before 1974, it was the modern tourist area of the city. Its inhabitants fled during the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974, when the city of Famagusta came under Turkish control, and it has remained abandoned ever since. As of 2019, the quarter continues to be uninhabited; buildings have decayed, and, in some cases, their contents have been looted over the years; some streets have been overgrown with vegetation; and the quarter is generally described as a ghost town.
The name of Varosha derives from the Turkish word Varog (suburb in English). The walled city of Famagusta was a precious and popular area before almost 100 years ago. The place where Varosha is located now was empty fields in which animals grazed. Ottoman Turks used the word Varos as the neighborhood just outside the castles.
The city was founded around 274 BC, after the serious damage to Salamis by an earthquake, by Ptolemy Philadelphus and named “Arsinoe” after his sister. Arsinoe was described as a “fishing town” by Strabo in his Geographica in the first century BC. It remained a small fishing village for a long time. Later, as a result of the gradual evacuation of Salamis due to the Arab invasion led by Muawiyah |, it developed into a small port.
Medieval Famagusta The old town is nicknamed “the city of 365 churches” owing to a legend that at its peak, Famagusta boasted one church for each day of the year. The walled city of Famagusta contains many unique buildings. Famagusta has a walled city popular with tourists.

Route Part 1
Discover The Ghost Town with Mr. John

The name Ayia Napa is derived from a Venetian-era monastery of the same name, located in the center of the town, next to the square that today is the clubbing centre.l2l The word “Ayia” means “holy” in Greek. “Napa” is archaic and means “wooded valley” or “dell”. In ancient times the area surrounding the town was covered with thick forest.
Ayia Napa lies near Cape Greco at the eastern part of Cyprus, south of Famagusta, and forms part of a larger area known as Kokkinochoria (“Red Villages”, a name derived from the vivid red colour of the soil). It is a town of the Famagusta District, in the remaining Greek-controlled southern part of the district, while the northern part has been occupied by Turkish forces since
1974.
Ayia Napa is about 12 kilometres (7.5 miles) from Protaras, a town that has seen similar development but still manages to remain low-key and more favourable for families and Cypriot locals.
Protaras (Greek: [Προταράς ]) is a predominantly tourist resort which comes under the administrative jurisdiction of Paralimni Municipality in Cyprus. In ancient times, where Protaras is now located, stood the old city-state of Leukolla.ll The city possessed a small safe harbour where Demetrius Poliorketes sought refuge in the year 306 BC, lying in wait for Ptolemy, one of the successors of Alexander the Great. Protaras is also referred to as “the land of windmills”, maintaining the nostalgic quality of the past.
Protaras has clear sky-blue waters and sandy beaches, the most well-known of which is Fig Tree Bay. Building on the success of Ayia Napa, located about 10 km (6 mi) southwest, it has expanded into a modern holiday resort of considerable size with tens of high capacity hotels, hotel apartments, villas, restaurants, pubs and associated facilities.
Protaras is a diving destination. Green Bay is the most popular dive site with thousands of first timers trying scuba skills Protaras most famous dive site for Technical Diving and Commercial Diver training is the Cyclops bay located on the border with Ayia Napa.
Kapparis is a coastal village in Cyprus near Paralimni and Protaras, and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) and part of the Famagusta district.
lt is a relatively new tourist town and under heavy construction and development of buildings, therefore, most buildings are new. There are some air raid shelters at Kapparis built during the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974.
Visitors from the UK and Greece come to the village on holiday, and there are a number of places to eat. There are several beaches in Kapparis including the famous beach called Fireman’s Beach.
*Kapparis is part of the Famagusta district which still a divided district and much of the area in Famagusta is occupied by TurkeyTurkey. The coastal road in Kapparis is called Kennedy Ave. fireman Beach
Route Part 2
Take in the scenery with Mr. John

Paralimni (Greek: Παραλιμνι) is a town within the Famagusta District of Cyprus, situated on the island’s east coast. Since the Turkish invasion in 1974, it has increased in size and status, primarily due to the migration of refugees fleeing from the north. Many workers in the tourist sectors of Protaras and Ayia Napa live in Paralimni, which is now the temporary administrative centre of the Famagusta District and the biggest municipality of the district under the control of the internationally-recognised government of Cyprus.
«The word Paralimni means “by the lake”. Historically, the town was built on the shores of a shallow lake which filled with water only in the winter. At the beginning of the 20th century, the whole lakebed was reclaimed for agricultural purposes.
Paralimni has not always been where it is now, and was built originally on a hill situated between Deryneia and its present location.
Deryneia (Greek: Δερύνεια) is a large village in the island of Cyprus. It is located at the east side of the island, 2 km (1 mi) south of the city of Famagusta. The population of the village is 5,758 (October 2011 census) and it consists of a municipality since 1994. The current mayor is Andros Karayiannis. Since the 1974 Turkish invasion of Cyprus, around 75% of the village terrain is in Northern Cyprus. The village is 12 kilometers from the famous resort of Ayia Napa.
The “Ghost Town” of Varosha can be clearly viewed from the roof of the Cultural Centre, as can the craters from shells fired during the invasion in the field opposite.
+ The village has agricultural land around it, and is one of the “Kokkinochoria” (red villages) so called from the red soil. Potatoes are widely grown but Deryneia is famous for its strawberries and holds a biennial strawberry festival at the
football ground of Anagennisi Deryneia on the Dherynia to Sotira road. Gazimagusa.
It has been named after the Lusignan monks that lived in Panayia of Hortanion, a nearby monastery and they were called Fremenors, as the Cypriot author Nearchos Klerides mentions in his book “Villages and Cities of Cyprus”.
«The monks could not support themselves and in 1468 they turned to Jacob, the Lusignan King of Cyprus who gave them a substantial sum of money. The village of Frenaros has its own Byzantine churches.
«Two of them, the Agios Andronikos and the Archangelos Michael dated back to the 12th century. The church of Ayia Marina has also some interesting frescoes.
Route part 3
Discover The History of the Ghost Town Famagusta with Mr. John

Located less than ten kilometers west of Famagusta and adjacent to the British Bases of Saint Nicholas or “four miles” as many call them. The village is situated geographically where Kokkinohoria end and the plain of Mesaoria begins.
«During the Turkish invasion of 1974 was occupied by the Turks on 31/8/1974. For the name of the village there is no specific credible version, documented in any way. Further south is the current District St. George Acheritou where many people from Acheritou and refugees from the surrounding villages were installed. After the tragic events of 1974, many residents of Acheritou took refuge in SEDIGEP packing plant which is in the S.B.A area.
A temporary school was set up with the help of the minister of education and refugee volunteers. Later in 1976-1977, most people moved to the refugee Community of Ayios Georgios Vrysoulles as it was first named.
Ayios Nikolaos Station (also spelled Agios Nikolaos; Greek: Άγιος Νικόλαος, lit. “Saint Nicholas”) is a British military station and part of in the British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia in Cyprus.
It is a former village (Ayios Nikolaos, SBA) connected by a road to the main area of the Dhekelia Garrison.
The Joint Service Signal Unit (Cyprus) (JSSU(Cyp)), formerly 9th Signal Regiment and the Royal Air Force’s 33 Signals Unit, is based at Ayios Nikolaos. This unit is a British Armed Forces run electronic intelligence gathering station. The station was established at Ayios Nikolaos shortly after the Second World War.
al 7
Before 1974, it was the modern tourist area of the city. Its inhabitants fled during the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974, when the city of Famagusta came under Turkish control, and it has remained abandoned ever since. As of 2019, the quarter continues to be uninhabited; buildings have decayed, and, in some cases, their contents have been looted over the years; some streets have been overgrown with vegetation; and the quarter is generally described as a ghost town.
The name of Varosha derives from the Turkish word Varog (suburb in English). The walled city of Famagusta was a precious and popular area before almost 100 years ago. The place where Varosha is located now was empty fields in which animals grazed. Ottoman Turks used the word Varos as the neighborhood just outside the castles.
The city was founded around 274 BC, after the serious damage to Salamis by an earthquake, by Ptolemy Philadelphus and named “Arsinoe” after his sister. Arsinoe was described as a “fishing town” by Strabo in his Geographica in the first century BC. It remained a small fishing village for a long time. Later, as a result of the gradual evacuation of Salamis due to the Arab invasion led by Muawiyah |, it developed into a small port.
Medieval Famagusta The old town is nicknamed “the city of 365 churches” owing to a legend that at its peak, Famagusta boasted one church for each day of the year. The walled city of Famagusta contains many unique buildings. Famagusta has a walled city popular with tourists.
